An Overview of Trust Registration
In India, Trust Registration is a process of permitting the Trust Deed from the Registrar of the respective jurisdiction. Trust Deed is a legal contract between the Settlor and Trustee and this is the primary requirement in the process of Trust Registration. In India, Trust Registration is done by the Trust Act, 1882 and in India, most Trust is incorporated as Public Charitable Trust, a form of a not-for-profit entity and these Trusts can be established for various purposes, including the social service, health care, education, provision of facilities for recreation and any other 0bject of general public welfare.
What is a Trust?
A Trust is an arrangement where the owner or Trust or of Trust transfers the property to a trustee. Such transfer of property is done for the benefit of a third party. The property is transferred to the Trustee by the Trust or along with a proclamation that the property should be held by the Trustee for the beneficiaries of the Trust. The Indian Trust Act 1882, provides for the provisions related to Trust in India. The Trust Registration is advisable in India for obtaining the benefits.
Different Types of Trusts in India
1. Public Trust: A Public Trust is one whose beneficiaries include the common public at large. Furthermore, a Public Trust in India can be further subdivided into Public Religious Trust and Public Charitable Trust.
2. Private Trust: In India, a Private Trust is one whose beneficiaries include individuals or families. Furthermore, a Private Trust in India can be subdivided into the following categories:
- A Private Trust whose beneficiaries and requisite shares both can be easily determined;
- A Private Trust whose both or either the beneficiaries or requisite shares cannot be easily determined.
Benefits of Trust Registration in India
- The primary reason behind creating a Trust in India is to indulge in some charitable activities and, at the same time, also avail of the benefits of tax exemption. These charitable trusts are also called Non-Profit Organisations.
- Trust can be used to allocate precise assets like land or an interest in the entity formed by the family, which otherwise wouldn't be practical for a trustor to split between individuals.
- When a person and his family move to another country, it's a perfect event to set up a Trust to get rid of taxation in the destination country, thereby protecting the family assets & providing flexibility in its organisation.
- The registered Trust facilitates the much-required financial help to the poor people & the masses through charitable activities.
- Anyone can leverage Trust Registration as a tool for transferring an asset to the heir in the absence of a Will. As the title of the assets transfers from the Settlor to the Trustee in case they are settled, there is no alteration of ownership after settlor demise, hence, evading the necessity for probate of a will onTrust assets account.
Some Vital Documents Required for Trust Registration
Following are some vital documents required at the time of Trust Registration in India:
- Identity proof to identify for Trustee and Trustor such as Driving License, Aadhar Card, Voter Id, Passport, etc.;
- The objective of Trust Deed;
- Latest photos of Trustee & Settlor;
- PAN details;
- NOC (No Objection Certificate) from the landlord, if the property is rented;
- Address proof of registered offices such as a copy of property or latest utility bills;
- Trust Deed on proper stamp value;
- Information of Trustee & Settlor such as self-attested copy id & address proof & occupation;
- Trust Deed must show the following details:
- Number of Trustees;
- Proposed name of Trust;
- The registered address of Trust;
- Proposed rules that will govern the Trust;
- Presence of Settlor and 2 witnesses during Trust Registration.
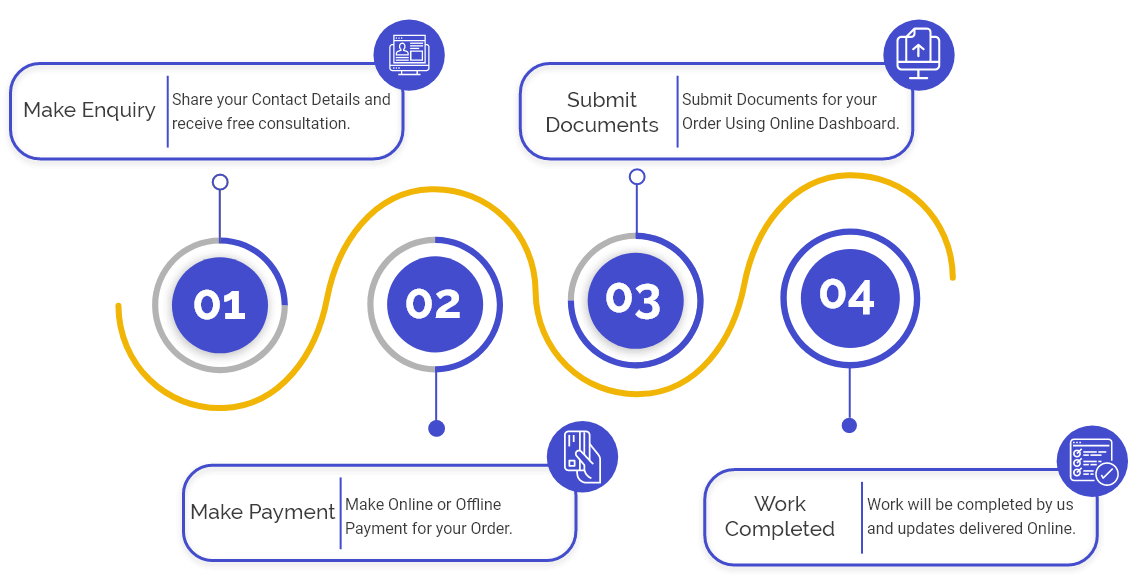
Procedure for Registering a Trust in India
Following is the detailed procedure for Trust Registration in India:
Step 1: Choose an appropriate name for Trust: This is the first step in the procedure of Trust Registration in India. Additionally, the name so suggested by the applicant should not come under the restricted list of the names as per the provisions of the Emblems and Names Act, 1950.
Step 2: Drafting of Trust Deed: The next step is drafting of the Trust Deed is vital because it's the only thing that makes the Trust legally enforceable. Generally, the Trust Deed consolidates the below-mentioned clauses:
- Acceptance of Funds: This enables the Trust to accept donations, subscriptions, and contributions from any individual, the Government Body or Charitable Avenue, in the form of cash or immovable assets without any alteration on it. Moreover, the clause states that any contributions that hinder the object of the Trust are non-acceptable in nature.
- Objects: This clause shows the object behind the formation of the Trust.
- Power of the Trustees: This clause specifies the responsibilities of the Trustees.
- Accounts and Audit: This mandates the trustees to administer the book of account on a regular basis. Moreover, it also sets the necessity for account auditing that must be conducted by a certified Chartered Accountant (CA).
- Winding Up: A Trust is wound up when all of the Trust assets are legally distributed to the beneficiaries/to a similar entity, either directly or through resettlement. The involved parties must identify any tax obligation incurred owing to the transfer of assets when the Trust is wound up. Moreover, this clause renders the necessity of conducting such a legal undertaking with the approval of the charity commissioner or court or any other law to mitigate any chances of legal dispute.
Penalties for Breaching Compliances of Trust Registration
- Tax Deduction Account Number Application: The Trust should make the official request before the Assessing officer for the allotment of the Tax Deduction Account Number after the registration of the Trust. For this, Trust can use the Form-49B facilitated by the IT Department. The TD Account Number should be quoted on all the challans for payment of sum u/s 200 & TDS certificate as well as returns delivered u/s 206, 206A & 206B. Section 272BB states the penalty to be imposed on the Trust for failing to avail of the TD Account Number and this section levied the penalty of Rs. 10,000/- in the aforementioned events.
- Civil & Criminal Penalties: The violation of the Trust Deed provisions incurs both civil & criminal penalties for the defaulters. Sections 405 to 409 of the IPC 1860 set out the provisions concerning the criminal violation of Trust.
- Failure in ITR Filing: Failure to file ITR attracts severe penalties under the Act. The income return shall not stand invalid if the TDS has not been provided along with the income return owing to the default of the taxpayer not rendering such certificate. The taxpayers are required to produce this certificate within 2 years from the end of the assessment year.
Frequently Asked Questions
In India, trust is more like an akin to a legal arrangement between the author and the trustee.
No, a registered Trust is not a separate legal entity, unlike a company.
Yes, Under Section 77 of the Indian Trust Act, 1882, a Trust can be terminated or extinguished if the purpose of the registered Trust becomes unlawful.
Yes, a revocable Trust in India can be dissolved, but as per the terms and conditions specified in the trust deed.
Trusts are usually set up for personal purposes or private purposes, whereas, on the other hand, the Corporations are set up for business and profit purposes.
In India, Trust has beneficiaries, who are the people for the benefit of whom the trust is established and will be handled.
Trustor or Settlor prepares the Trust Deed in India.
Settlor, Trustee, and Beneficiaries are the 3 parties of a Trust.
Yes, it is compulsory to get a Trust registered in India.
Yes, a revocable Trust Deed can get amended.
The steps involved in the process to register Trust in India are Choose an Appropriate Name; Decide the Authors and Trustees; Formulate MOA and Trust Deed; Preparation of Trust Deed on a Stamp Paper; Submission of Trust Deed to the Registrar; Obtain the Certificate of Registration.
The Indian Trusts Act, 1882, is the governing law for a Trust in India.
The 2 different types of Trust are Private Trust and Public Trust.
The key duties of a Trustee are Fiduciary Duty; Duty of Care; Duty of Intimating the Beneficiary of any Form of Changes made in the Trust; and the Duty to Administer the Trust Property.
The person who creates the trust is a Trustor. In contrast, the person who has the responsibility of managing the trust for the beneficiary is known as Trustee.
Both civil and criminal penalties may be imposed on the Beneficiary for Breach of Trust.
Yes, the working and operations of an NGO and Trust are the same.
A Trust already operating cannot close its operations and management. However, in the case of disqualifications on shareholders, trust can be closed.